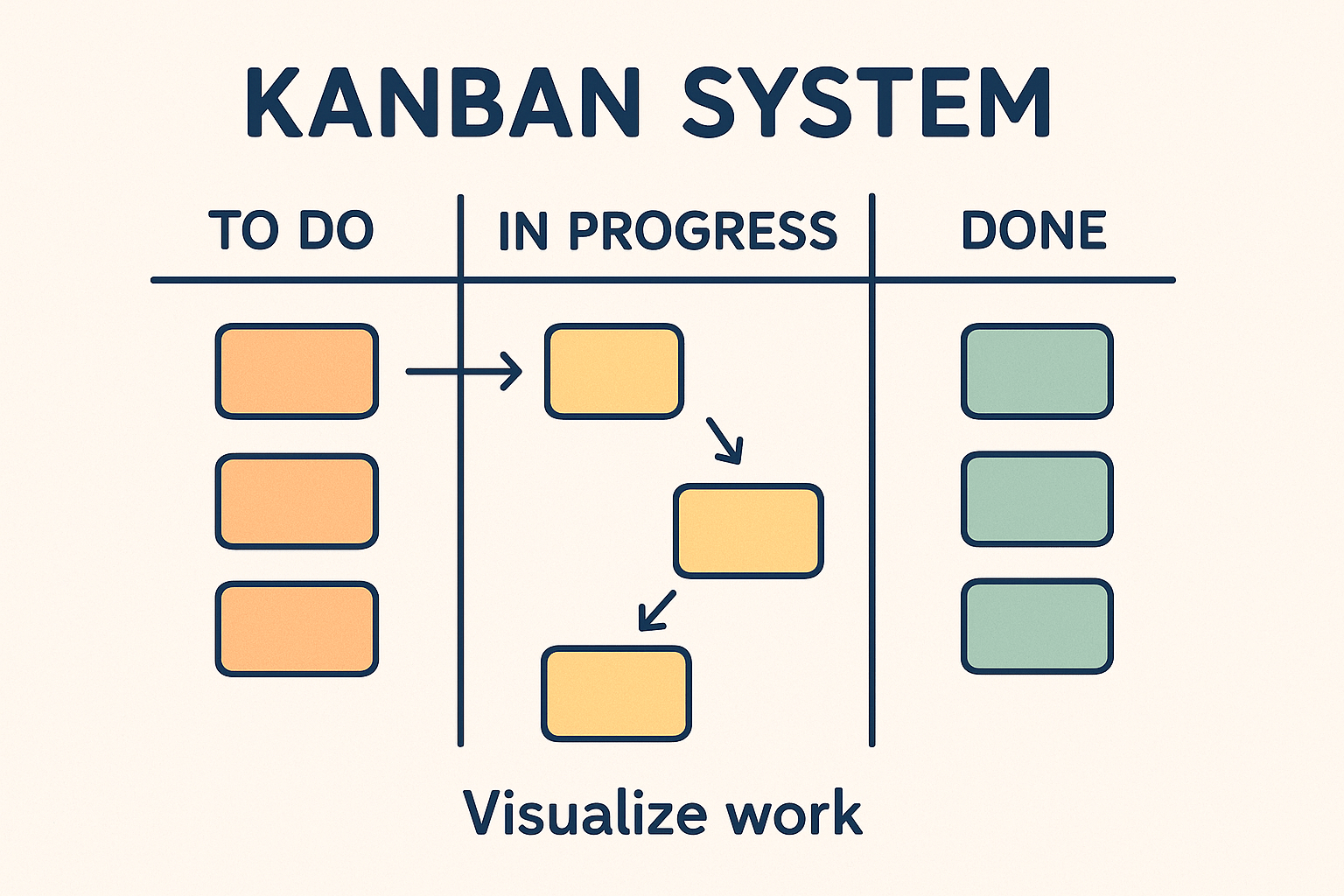
The Kanban system, originally developed by Toyota, is a dynamic project management approach designed to visualize and optimize workflow. It uses a visual board divided into columns such as “To-Do,” “In-Progress,” “Validation,” and “Done,” allowing teams to track tasks seamlessly through each phase.
Widely adopted in software development and beyond, Kanban promotes continuous delivery, incremental improvements, and greater transparency. By fostering adaptability and streamlining processes, it enhances productivity and efficiency across diverse industries.
In this article, we’ll explore the Kanban system in detail its principles, structure, and how it empowers teams to work smarter and deliver better results.
What is Kanban?
Kanban is a visual workflow management system designed to help teams manage, track, and optimize their work processes. By visualizing tasks, limiting work in progress (WIP), and adopting a pull-based approach, Kanban fosters continuous improvement and ensures smoother project flow.
As an effective process management tool, Kanban enhances team productivity and efficiency. Its visual design, flexibility, and focus on limiting WIP make it adaptable across various industries and team structures. Whether used in software development, marketing, or personal productivity, Kanban helps teams stay organized, collaborative, and focused on delivering consistent results.
Understanding the Kanban System
The Kanban system is a visual workflow management approach designed to enhance team productivity, streamline processes, and improve overall efficiency. Rooted in Toyota’s production methodology, Kanban is built on key principles visualizing work, limiting work in progress (WIP), and optimizing flow.
It emphasizes continuous improvement and adaptability by allowing teams to pull tasks through a defined process, ensuring that each task is completed effectively and efficiently. A central element of this system is the Kanban board, which promotes transparency and collaboration. On the board, tasks are represented as cards and organized into columns that reflect different workflow stages.
What is a Kanban Board?
A Kanban Board is a visual project management tool used to track, organize, and optimize workflow. It consists of cards representing individual tasks and columns indicating the various stages of a process - such as To Do, In Progress, Review, and Done.
Originating from lean manufacturing in Japan, the Kanban method has evolved into a powerful Agile project management framework, widely used in software development, project management, and manufacturing. By focusing on visibility, flow, and continuous improvement, Kanban boards help teams manage work efficiently and deliver consistent, high-quality results.
How a Kanban Board Works?
A Kanban board functions by visually mapping out the flow of work items as they move through different stages of a process. It helps teams monitor progress, maintain focus, and continuously improve workflow efficiency. Here’s how it typically operates:
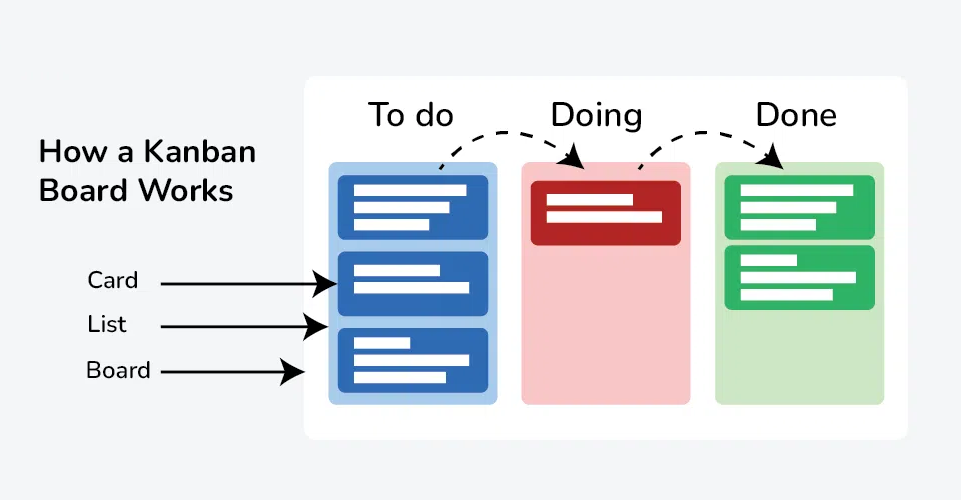
1. Initiation: Tasks are created and added to the “To Do” column, representing the backlog or pending work that needs attention.
2. Progression: As work begins, task cards move across the board through stages such as “In Progress,” “Review,” or “Testing,” visually reflecting their current status and ensuring clear team visibility.
3. Completion: Once finished, tasks are moved to the “Done” column, signifying successful completion. The goal is to maintain a consistent and balanced flow of tasks through each stage.
4. Continuous Improvement: Teams regularly conduct reviews and retrospectives to analyze workflow performance, identify bottlenecks, and make process enhancements—ensuring continuous improvement and sustained productivity.
Understanding Electronic Kanban Systems
Traditional Kanban boards have evolved into Electronic Kanban Systems (eKanban)—digital platforms that use software tools to visualize, track, and manage workflow in real time. These systems enhance the accessibility and flexibility of Kanban principles, making them ideal for remote teams and complex projects.
By digitizing the classic Kanban framework, eKanban systems provide an innovative and adaptable way to streamline operations, strengthen collaboration, and boost overall productivity. They enable teams to visualize work, communicate effectively, and leverage data-driven insights to support continuous improvement and smarter decision-making.
The 6 Core Practices of the Kanban Method
The Kanban methodology is built on six fundamental practices that guide teams toward operational excellence:
1. Visualize Workflow: Make work visible by representing tasks as cards on a Kanban board, with columns depicting stages from idea to completion. This transparency helps everyone understand the current state of work.
2. Limit Work in Progress (WIP): Set limits on the number of tasks allowed in each workflow stage. WIP limits help prevent overload, reduce bottlenecks, and maintain a steady pace of progress.
3. Manage and Optimize Flow: Focus on maintaining a smooth and sustainable flow of work. Prioritize consistent value delivery and avoid overburdening the team, which can affect quality and morale.
4. Establish Clear Process Policies: Define and communicate process rules such as Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), “Definition of Ready,” and “Definition of Done.” Clear guidelines ensure shared understanding and smooth task progression.
5. Implement Feedback Loops: Regular reviews, meetings, and performance checks help teams identify issues, adapt processes, and drive ongoing improvements through constructive feedback.
6. Foster Collaborative Evolution: Empower teams to take ownership of their workflow. Encourage experimentation, teamwork, and incremental changes that promote continuous learning and process enhancement.
Together, these core practices make Kanban a powerful, flexible framework for managing work, driving efficiency, and fostering a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement.
How does Kanban Work?
In Kanban, teams start by visualizing their existing processes and then continuously refining them to achieve greater efficiency. The Kanban framework built on its core values, principles, and practices—encourages adaptability, transparency, and ongoing improvement, helping teams create more effective and streamlined workflows.
A classic Kanban board typically consists of three main columns that represent different stages of work:
1. To Do
This column contains tasks that haven’t been started yet—essentially, the backlog. It’s where all upcoming work items are listed, waiting to be picked up.
Think of it as the starting zone where ideas and plans are organized before action begins. Just like backstage before a performance, tasks here are being prepped and prioritized for execution.
2. Doing
The “Doing” column represents tasks that are currently in progress. Once a team member begins working on a task—whether coding a new feature, designing an interface, or writing content—it moves from “To Do” to “Doing.”
This stage is the heartbeat of productivity, where ideas take shape and progress becomes visible. It’s where the team focuses their efforts, ensuring work flows smoothly toward completion.
3. Done
The “Done” column represents tasks that have been successfully completed—it’s the final stage of the workflow. Each card here symbolizes progress, achievement, and the culmination of effort.
Think of it as the victory zone where completed tasks take center stage. When a developer or team member moves a task to “Done,” it signals that the work is finished, reviewed, and ready for delivery or deployment. It’s a visual reminder of productivity and teamwork—every completed task is a small celebration of success.
Is Kanban Agile or Lean?
Kanban is primarily rooted in Lean principles, but it’s also widely used within Agile frameworks.
Lean:
Kanban aligns closely with Lean thinking, focusing on eliminating waste, optimizing workflow, and maximizing efficiency. It promotes continuous improvement and emphasizes delivering value to the customer by streamlining processes.
Agile:
While Kanban isn’t exclusive to Agile, it integrates seamlessly with Agile methodologies to manage workflows, enhance flexibility, and support iterative delivery. It complements Agile practices by offering a visual system that helps teams plan, track, and adapt in real time.
In essence, Kanban bridges both worlds—it can be seen as a Lean tool for process optimization and an Agile practice for adaptive, incremental work management.
KANBANF Certification
Understanding the Kanban System is one thing. Being able to prove that you can effectively apply its principles and practices in a professional setting is another. This is where a formal certification becomes invaluable.
The KANBANF: EXIN Kanban Foundation certification is a globally recognized credential that validates your foundational knowledge of the Kanban method.
Why Pursue the KANBANF Certification?
According to EXIN, the official certification body, the KANBANF: EXIN Kanban Foundation certification is designed for any professional involved in work that can be improved by a flow-based system. This includes:
- Project and Program Managers
- Software Developers, Testers, and IT Managers
- Business Analysts
- Marketing Managers
- HR Professionals
The certification covers the core concepts, principles, and practices of the Kanban System—from its history and Lean-Agile connections to the practical application of boards, WIP limits, and flow metrics.
Bridge the Gap from Knowledge to Certification
The journey to certification can feel like a complex workflow with its own bottlenecks. You can read all the articles and books, but the exam itself presents a unique challenge. The stress of not knowing what to expect, the fear of failing, and the time spent searching for reliable study materials can be overwhelming. This is where you need a clear path to "Done."
This is why mastering the concepts isn't enough. You need to simulate the exam experience.
Our KANBANF practice exams are designed to move your preparation from "In Progress" to "Certified." These practice tests are your feedback loop. They are built to mirror the official EXIN KANBANF syllabus and exam format, helping you:
- Identify Bottlenecks: Discover your "knowledge gaps" in specific areas.
- Manage Your Flow: Practice your exam-taking time (your 'cycle time'!), ensuring you can answer all questions confidently within the allotted period.
- Make Your Policies Explicit: Solidify your understanding of key terms and practices.
- Build Confidence: Reduce exam-day anxiety by knowing you've successfully navigated the format and question types before.
Don't leave your certification to chance. Use a proven system of practice, feedback, and continuous improvement to ensure your success.
Conclusion
The Kanban approach is simple, flexible, and highly adaptable—making it ideal for teams across industries, from software development to project management. By implementing Kanban principles, organizations can experience increased productivity, shorter lead times, and stronger collaboration.
Ultimately, Kanban fosters a more agile, efficient, and resilient work environment, empowering teams to deliver value continuously and adapt to change with confidence.











Write a comment ...