
The digital-first world runs on software, and the engine that builds, delivers, and maintains that software at high speed is DevOps. It’s not just a job title or a piece of technology; it’s a cultural shift that has become the single most critical factor for modern business success. If you're a tech professional or an aspiring one looking for a career that is challenging, in-demand, and highly lucrative, you’ve found it.
But what does a career in DevOps actually look like? It's a vast landscape of different specializations, from safeguarding infrastructure to automating entire software pipelines. This guide is your map. We will explore the core of DevOps, break down the 10 most popular career paths, examine the impressive salaries you can command, and show you how to formalize your skills with the EXIN DevOps Professional certification.
What is DevOps?
At its simplest, DevOps is a cultural philosophy, a set of practices, and a collection of tools that breaks down the traditional barriers between software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops).
In the "old days," developers wrote code and "threw it over the wall" to the operations team, who were then responsible for deploying and maintaining it. This created friction, blame games, and painfully slow release cycles.
DevOps merges these two worlds. It’s a continuous loop where teams collaborate across the entire software lifecycle, from planning and coding to testing, releasing, deploying, operating, and monitoring.
This philosophy is built on a few key principles, often called "The Three Ways":
Flow: This is all about accelerating the workflow from Dev to Ops. The goal is to get new features and fixes to the customer as quickly and reliably as possible. This is achieved through automation, continuous integration (CI), and continuous delivery/deployment (CD).
Feedback: This principle emphasizes creating fast and constant feedback loops from Ops back to Dev. By monitoring applications in production, teams can instantly identify bugs, performance issues, or user-stuck points and feed that information back into the development cycle.
Continual Learning & Experimentation: This is the cultural heart of DevOps. It fosters a high-trust environment where teams are encouraged to experiment, take calculated risks, and learn from failure. Instead of punishing outages, teams conduct "blameless post-mortems" to find the root cause and improve the system for everyone.
By embracing this culture, companies can release higher-quality software faster, respond to market changes instantly, and create more stable and reliable systems.
Why Choose DevOps for Your Career?
A career in DevOps is more than just a good job; it’s a ticket to the front lines of technological innovation. The demand for professionals who can bridge the gap between development and operations has never been higher, and it continues to grow as more companies—from tiny startups to Fortune 500 giants—undergo digital transformation.
Here’s why DevOps is a smart, future-proof career choice:
- Massive Job Demand: The 2024 DevOps Institute "Upskilling" report highlights a persistent and growing skills gap. Companies are desperately seeking qualified DevOps professionals, meaning you have significant leverage in the job market.
- High-Impact Work: DevOps roles are not support functions. You are central to the business's ability to innovate and deliver value. The pipelines you build and the systems you stabilize are the direct pathways for revenue and customer satisfaction.
- Exceptional Salaries: As you'll see in our salary section, DevOps professionals are among the highest-paid in the tech industry. This reflects the immense value and complex skillset the role demands.
- Continuous Learning: This field is the opposite of stagnant. You will constantly be working with new tools, cloud platforms, and methodologies. If you have a curious mind and love to solve puzzles, you will never be bored.
- Multiple Career Paths: DevOps is not a single, linear track. It’s a tree with many branches. You can specialize in security (DevSecOps), reliability (SRE), cloud platforms, or automation. This guide will explore 10 of those exciting paths.
- Cultural Importance: DevOps professionals are agents of change. You don't just manage machines; you help improve processes, foster collaboration, and build a better, more efficient engineering culture.
Popular Career Paths in DevOps
The term "DevOps Engineer" is often used as a catch-all, but the reality is a rich ecosystem of specialized roles. Here are 10 of the most common and in-demand careers you can pursue under the DevOps umbrella.
1. DevOps Engineer
This is the foundational role. A DevOps Engineer is a generalist who understands the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC). Their primary job is to build and maintain the Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline. They are the glue that holds the development and operations teams together.
- Core Responsibilities: Building automated build/test/deploy pipelines (using tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions), managing version control (Git), and scripting (Bash, Python, or Go).
- Key Skills: CI/CD tools, Git, scripting, and a good understanding of both development and system administration.
2. Site Reliability Engineer (SRE)
Coined at Google, the SRE role is what happens when you treat operations as a software engineering problem. An SRE's main goal is to create ultra-reliable, scalable, and high-performance software systems. They have a "service level objective" (SLO) for system uptime and spend their time automating, monitoring, and engineering solutions to prevent outages.
- Core Responsibilities: Setting and monitoring SLOs/SLIs, incident response and post-mortems, capacity planning, and writing software to automate operational tasks.
- Key Skills: Deep systems knowledge (Linux, networking), strong coding skills (Go, Python, C++), and mastery of monitoring and observability tools.
3. Cloud DevOps Engineer
This is a DevOps Engineer who specializes in a specific cloud platform. As most companies now run on public cloud infrastructure, this role is incredibly valuable. They are experts at using the services of a provider (like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud) to build, deploy, and scale applications.
- Core Responsibilities: Provisioning and managing cloud infrastructure, using cloud-native CI/CD services (e.g., AWS CodePipeline, Azure DevOps), and optimizing applications for cloud performance and cost.
- Key Skills: Deep expertise in AWS, Azure, or GCP; Infrastructure as Code (Terraform, CloudFormation); and containerization.
4. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Specialist
This specialist focuses on one thing: managing infrastructure through code. Instead of manually clicking buttons in a cloud console to create servers or databases, an IaC specialist writes definition files. This makes infrastructure provisioning repeatable, testable, and version-controlled, just like application code.
- Core Responsibilities: Writing and maintaining Terraform or Ansible modules, creating reusable infrastructure blueprints, and ensuring infrastructure compliance and security.
- Key Skills: Mastery of Terraform and/or Ansible, deep understanding of cloud networking and security, and strong scripting abilities.
5. Release Manager
In a fast-paced DevOps environment, a Release Manager is the project manager for software releases. They coordinate all the moving parts to ensure that new code gets to production smoothly and safely. They manage release schedules, coordinate between different teams (dev, QA, ops), and manage the risks of deployment.
- Core Responsibilities: Planning and scheduling releases, managing the CI/CD pipeline from a high level, communicating with stakeholders, and implementing deployment strategies (like blue-green or canary releases).
- Key Skills: Strong project management, excellent communication, a deep understanding of the SDLC, and familiarity with Git branching strategies.
6. Containerization Specialist
This role, often called a "Kubernetes Engineer" or "Docker Specialist," focuses on packaging applications into containers and managing them at scale. Containers (like Docker) solve the "it works on my machine" problem, and orchestration platforms (like Kubernetes) run those containers reliably across thousands of servers.
- Core Responsibilities: Creating and optimizing Dockerfiles, building and managing Kubernetes clusters, setting up service mesh (like Istio), and helping developers "containerize" their applications.
- Key Skills: Expert-level Docker and Kubernetes, cloud-native networking and storage, and a solid grasp of microservices architecture.
7. Security Engineer (DevSecOps)
This is one of the fastest-growing and most critical roles in DevOps. A DevSecOps Engineer is responsible for "shifting security left"—integrating security into every step of the development pipeline, rather than waiting until the end. Their motto is "security at speed."
- Core Responsibilities: Integrating automated security scanning tools (SAST, DAST, IAST) into the CI/CD pipeline, managing secrets, auditing cloud infrastructure for compliance, and training developers on secure coding practices.
- Key Skills: Strong cybersecurity background, familiarity with compliance (SOC 2, PCI), and knowledge of pipeline security and cloud security tools.
8. Monitoring & Observability Engineer
While an SRE does monitoring, this specialist lives and breathes it. They go beyond simple "is the server up?" alerts. An Observability Engineer builds sophisticated systems to understand the internal state of an application. They answer complex questions like, "Why is this specific user's API call slow?"
- Core Responsibilities: Implementing the "three pillars of observability": logs, metrics, and traces. They manage tools like Prometheus, Grafana, OpenTelemetry, and Datadog.
- Key Skills: Deep expertise in monitoring tools, data analysis, and a strong understanding of distributed systems.
9. Automation Engineer
While all DevOps roles involve automation, this role is singularly focused on it. An Automation Engineer looks for any manual, repetitive, or error-prone task in the organization and automates it out of existence. This could be anything from user onboarding to system patching or infrastructure provisioning.
- Core Responsibilities: Writing scripts (Python, Bash, PowerShell), building "self-service" tools for other teams, and managing configuration management tools (Ansible, Puppet, Chef).
- Key Skills: Expert-level scripting, a "systems thinking" mindset, and a passion for efficiency.
10. Freelance DevOps Consultant
Once you have significant experience (5-10+ years) in one or more of these roles, you can become a freelance consultant. Companies hire you for short-term projects to solve specific, high-stakes problems: migrating them to the cloud, building their first CI/CD pipeline, auditing their security, or training their team.
- Core Responsibilities: Quickly assessing a client's technical environment, providing strategic recommendations, and executing on high-level projects.
- Key Skills: Deep technical expertise, strong business acumen, excellent communication and teaching skills, and self-management.
Average Salaries for DevOps Related Careers
DevOps is a field where your skills are directly and generously rewarded. Because you are a "force multiplier" who makes entire engineering teams more productive, your compensation reflects that value.
While salaries vary based on location (e.g., San Francisco vs. a smaller city), years of experience, and company size, here is a breakdown of typical average salary ranges for these roles in the United States.
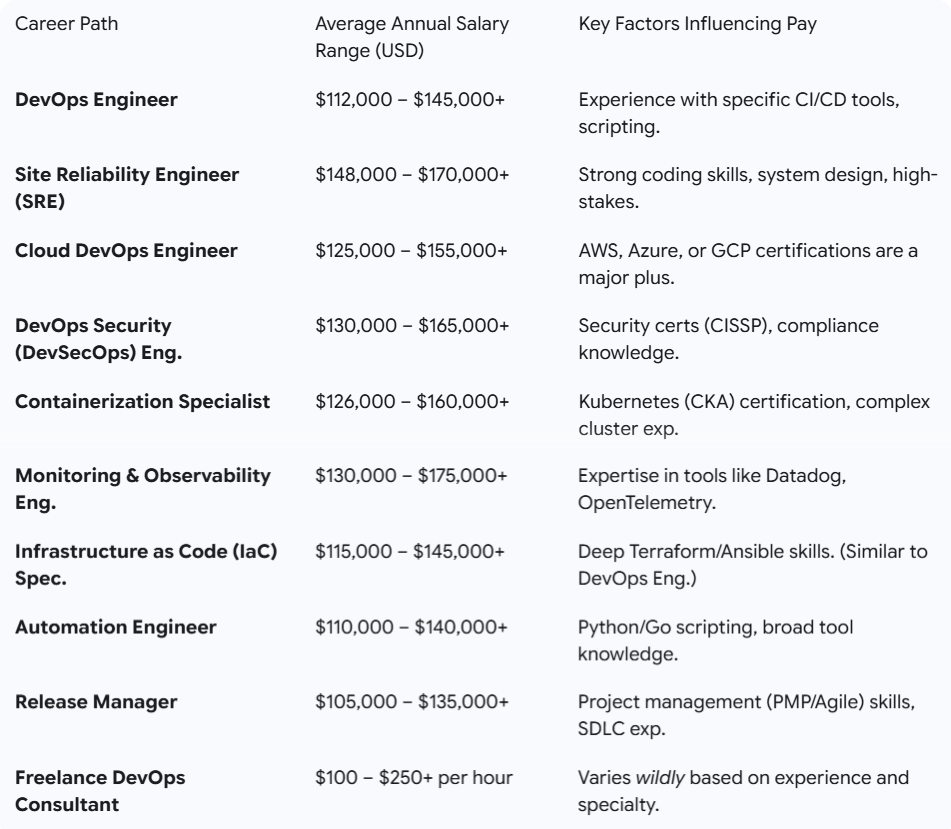
As you can see, these are some of the most lucrative positions in all of technology, with specialized roles like SRE, DevSecOps, and Observability often commanding the highest salaries.
The EXIN DevOps Professional Certification
You have the ambition. You see the career paths. Now, how do you prove you have the foundational knowledge to succeed? This is where a respected, vendor-neutral certification becomes invaluable. The EXIN DevOps Professional certification is designed to validate your understanding of the core principles and practices of DevOps.
This certification is not just another piece of paper. It serves as a crucial stepping stone, especially for those transitioning from traditional IT, development, or project management roles. It proves to employers that you speak the language of modern software delivery.
What Does the EXIN DevOps Professional Cover?
This certification is based on the official EXIN body of knowledge, which aligns perfectly with the "Three Ways" philosophy we discussed. It focuses on the practical application of DevOps principles:
- DevOps Adoption: Understanding how to introduce and foster a DevOps culture in an organization.
- The First Way: Flow: Mastering the concepts of CI/CD, automation, and optimizing the value stream.
- The Second Way: Feedback: Implementing monitoring, logging, and testing to create fast feedback loops.
- The Third Way: Continual Learning: Fostering a culture of experimentation, blameless post-mortems, and continuous improvement.
- Information Security & Change Management: A key focus on integrating security and managing change in a high-speed DevOps environment (a nod to DevSecOps).
Who is this Certification For?
This certification is ideal for a wide range of IT professionals, including:
- Aspiring DevOps Engineers
- Software Developers
- System Administrators
- Agile and Scrum Practitioners
- IT Project Managers
- QA and Test Engineers
- IT Service Managers
Exam Details
- Exam Name: DEVOPSP: EXIN DevOps Professional
- Number of Questions: 40 Multiple-choice
- Pass Mark: 65% (26 out of 40)
- Exam Length: 90 minutes
- Books / Training: EXIN DevOps Program Vision and DevOps: The Next Generation - 3 Ways T-Shaped Skills are Important in DevOps Teams
How to Prepare for the DEVOPSP Exam
The thought of facing a 90-minute certification exam can be stressful. You have to balance your current job, your studies, and the pressure to pass on the first try. You might read the official guides and still wonder, "Am I really ready for the types of questions they'll ask?"
This is precisely where targeted practice becomes your greatest asset. Reading theory is one thing; applying it under exam conditions is another.
To bridge this gap, using a high-quality online practice exam platform is the most effective way to build confidence and ensure success. Platforms like CertFun offer a specialized DEVOPSP online practice exam that simulates the real testing environment.
By using realistic practice tests, you can:
- Identify Knowledge Gaps: Find out exactly which parts of the DevOps philosophy (like Flow, Feedback, or Security) you need to review.
- Master Time Management: Learn to answer 40 questions in 90 minutes, so you don't feel rushed on exam day.
- Reduce Exam Anxiety: The unknown is a major source of stress. By seeing the question formats and difficulty level beforehand, you eliminate surprises and can walk into the exam with confidence.
- Validate Your Readiness: When you consistently pass the practice exams, you know you're ready to book the real thing and invest your time and money wisely.
Don't leave your certification to chance. A small investment in realistic practice can make all the difference in launching your new DevOps career.
Conclusion
The DevOps movement is not a trend; it is the new standard for building and delivering software. It represents a fundamental shift towards collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement. For those willing to embrace this culture and learn the tools, the rewards are undeniable: a high-impact, high-paying, and intellectually stimulating career with endless opportunities for growth.
We’ve covered the core philosophy of DevOps, explored 10 diverse and exciting career paths, and seen the impressive salaries they command. We also identified a clear, actionable first step: validating your foundational knowledge with the EXIN DevOps Professional certification.
This is a field that rewards doers. The best way to start is to pick a tool, build a project, and formalize your learning. Your future as a high-impact DevOps professional is waiting.










Write a comment ...